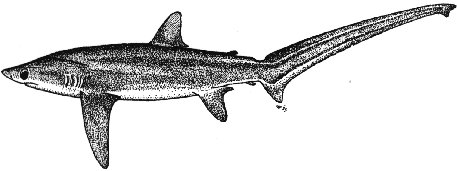
Bigeye thresher shark (Alopias superciliosus)
(Lowe, 1839)
| Fr |
Renard a gros yeux |
| Sp |
Zorro ojon |
| It |
Squalo volpe occhione; Falso volpe (Mazara
del Vallo); Volpe dall'occhio grosso (Sicily) |
| Ma |
Pixxivolpe Falz |
Diagnosis
Although superficially similar to A. vulpinus, this shark is very
readily distinct upon closer inspection. Trunk rather stout, with
the elongate caudal lobe nearly as long as rest of body; eyes
distinctly large, dorsally-orientated with a prominent dorsal groove
on the contours of the head above the gills. Snout short,
laterally flattened between eyes; no labial furrows at corners of
mouth. Anterior origin of 1st dorsal fin posterior to rear free tips
of pectoral fins. Pectoral fins rather more broad-tipped than A.
vulpinus. Dorsal colour grey-brown, with a somewhat bronzy
sheen on the flanks that may not always be distinct; ventrum shading
to lighter grey -white, with demarcation or blotchiness not
immediately apparent; no light pigment extending above the pectoral
fin bases.
Size
To about 461cm TL; typically 270cm to 430cm but Mediterranean
data scant; size at birth ca. 70 to 106cm.
Status and Distribution
Mediterranean Sea Rather infrequent or rare, with a
limited identified range, but cannot be considered accidental;
Western Mediterranean, from Gibraltar eastwards through the southern
Alboran Sea and particularly Morocco; other recent records from the
Sicilian Channel (landed at Mazara del Vallo); not yet reported from
Tunisia but can be considered as frequenting those waters; off
southern Malta towards Libya, the Central Ionian Sea and also
Tyrrhenian Sea (Tropea; Eolie Islands); perhaps more cosmopolitan in
deeper waters of the Central and Western Mediterranean.
Biology
An active epipelagic and epibenthic species, occurring from
coastal neritic waters to well offshore in the great ocean basins;
Mediterranean captures typically all over offshore continental shelf
waters where it occurs from the surface down to circa. 250m;
elsewhere recorded to at least 500m depth and considered a
habitually deeper swimmer and feeder than A. vulpinus. Like its
congener, the bigeye thresher is believed to utilise the elongate
tail as a feeding tool. Reported diet consists of pelagic bony
fishes including scombroids, clupeoids and small billfishes; hake
and cephalopods; no Mediterranean data but anecdotal reports from
Maltese fishermen suggest a strong association between these sharks
and highly mobile scombroids such as Auxis rochei. Ovoviviparous,
with 2 - 4 young per litter; females mature between 355 -
430cm; males between 270 - 400cm.
The Shark Trust, 36 Kingfisher Court, Hambridge Road, Newbury, Berkshire, RG14 5SJ, UK.
Tel(+44) 01635 551150, Fax(+44) 01635
550230
|