Little sleeper shark (Somniosus rostratus)
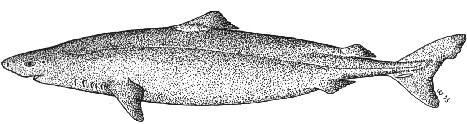
(Risso, 1826).
| Fr |
Laimargue de la Mediterranee |
| Sp |
Tollo boreal |
| It |
Lemargo; Erculiachilli imperiali di funnu
(Sicily) | Other scientific names
recently used: Somniosus bauchotae Quero, 1976.
Diagnosis
A moderately-sized, rather slender shark with two small, low
spineless dorsal fins; no anal fin and a small keel present upon the
ventral lobe of the caudal fin below the lateral line on the
peduncle. Lower caudal lobe relatively long. Head short, with
broadly-rounded snout and comparatively small eyes, with prominent
spiracles just behind them; teeth fairly large with semi-oblique
cusps. Skin feels rather smooth. Colour dark grey, brown or
olive-brown; no obvious fin markings.
Size
To about 140cm TL; size at birth between 21 and 28cm. Most
specimens typically to 100cm.
Status and Distribution
N.E. Atlantic: Infrequent or rare. Northerly limit of
range uncertain; recorded from off N.W. Ireland at ca. Latitude
55-56N; also in Bay of Biscay, off Portugal and Madeira; southwards
in deep water off the N.W. African coast south to the Canary
Islands; southerly range limit unclear.
Mediterranean
Sea: Infrequent or rare; Western Mediterranean with known
capture-sites including deepwater along the Cote d'Azur, Ligurian
Sea, Eastern Sicily and Algeria. Apparently not yet recorded from
Malta but a likely addition to their elasmobranch fauna. Probably
extremely scarce or even absent eastwards of the Ionian Sea.
Biology
This little-known deepwater shark is probably benthopelagic,
rather than benthic, based upon its specialised heterocercal tail
which is markedly different from both coastal and deepwater benthic
species. The presence of caudal keels also suggest adaptions for
active predation upon mobile prey, rather than a sedentary habit as
displayed by its larger congener, S. microcephalus. The little
sleeper shark occurs at depths of 400+ metres in Atlantic waters and
between 250 to 1000m in the Mediterranean, near to or on the seabed,
both offshore and in deep coastal waters such as the Ligurian Sea. A
predator of deepwater telosts and invertebrates, little is known of
its feeding habits. Ovoviviparous, with between nine and seventeen
embryos found in Mediterranean females. Females mature from 82 to
134cm TL; males from 71 cm.
The Shark Trust, 36 Kingfisher Court, Hambridge Road, Newbury, Berkshire, RG14 5SJ, UK.
Tel(+44) 01635 551150, Fax(+44) 01635
550230
|